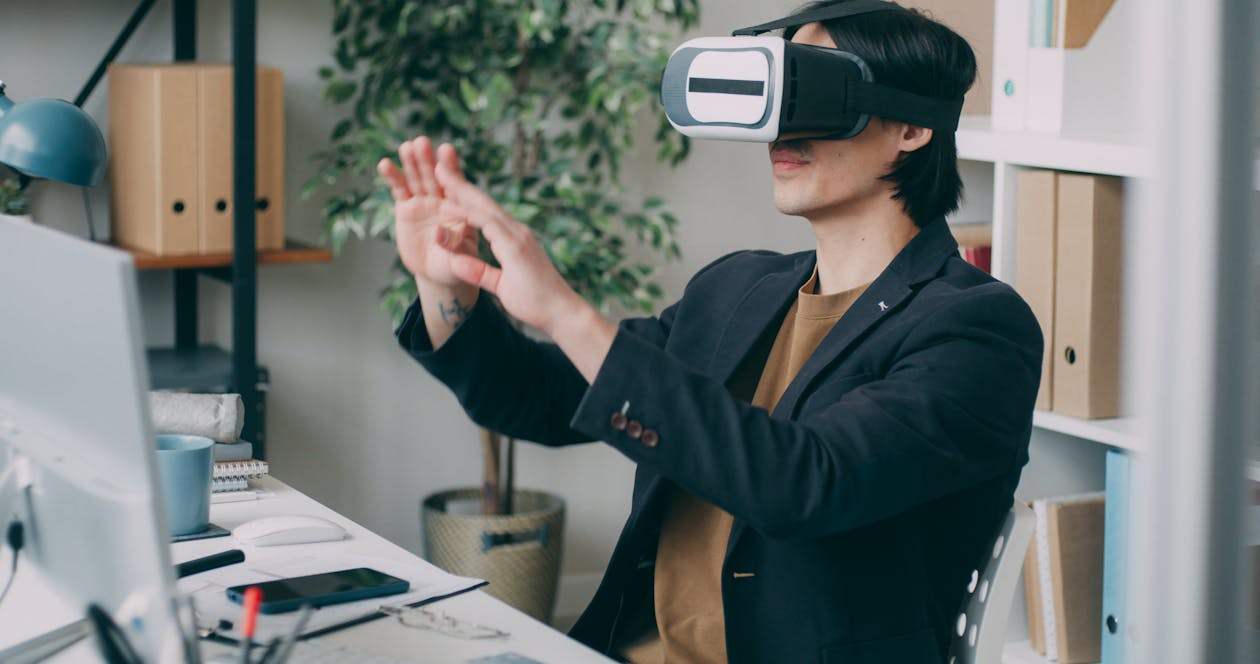
The metaverse is often associated with virtual reality headsets and online gaming worlds. However, its potential reaches far beyond entertainment, with growing interest in the metaverse economic impact on education, healthcare, business, and global trade.
As digital ecosystems become increasingly immersive and interconnected, the metaverse is emerging as a new economic frontier with significant real-world implications. Companies, governments, and investors are exploring how virtual environments can transform everything from remote work to international trade, signaling a future where digital spaces become an integral part of everyday life.
A New Layer of the Global Economy
The metaverse represents a persistent, shared digital world where users interact through avatars, virtual objects, and AI-driven environments. Unlike traditional websites or apps, these virtual spaces are immersive, three-dimensional, and capable of hosting complex social and economic activity.
Corporations are already establishing virtual offices where employees collaborate across continents without the limitations of physical distance. Educational institutions are experimenting with virtual campuses that provide hands-on learning through simulations, allowing students to conduct science experiments, practice medical procedures, or explore historical environments in ways impossible in a typical classroom.
Industries such as automotive, architecture, and manufacturing use the metaverse to build digital twins. These are virtual replicas of physical products used for real-time testing and development. These tools accelerate design, reduce costs, and improve quality while connecting global teams in shared virtual workspaces.
In this sense, the metaverse is becoming a powerful extension of the global economy, enabling new forms of productivity and innovation.
See The Digital Divide for insights into who may gain or miss out on metaverse access.
Transforming Healthcare, Training, and Professional Work
Beyond business collaboration, the metaverse is driving advancements in healthcare. Surgeons are using virtual-reality simulations to practice complex procedures, improving precision and reducing patient risk. Medical students can observe virtual surgeries from any location, enhancing access to specialized training. Therapists are adopting VR-based treatments for anxiety, PTSD, and pain management—demonstrating how immersive experiences can reshape mental and physical healthcare.
Workplace training is also being revitalized. Aviation, construction, and energy companies use virtual simulations to train employees without exposing them to real-world hazards. Complex tasks such as equipment repair, disaster response, and emergency management can be practiced safely in highly realistic digital environments.
These applications showcase the metaverse’s promise as a tool for skill development, safety, and professional excellence across numerous industries.
Check out How AI Translation Is Breaking Down Language Barriers to see how tech tools reshape global collaboration.
A Marketplace for Digital Goods and Global Creativity
The metaverse is also giving rise to new economic models centered on digital goods and services. Virtual fashion, art, real estate, and entertainment experiences now represent a multi-billion-dollar market. Brands such as Nike, Gucci, and Adidas have launched virtual collections, enabling users to outfit their avatars with designer apparel.
Musicians and creators are hosting virtual concerts and events attended by millions, generating revenue without the geographical or logistical constraints of physical venues. Meanwhile, virtual real estate developers build interactive worlds for commerce, social gatherings, or branded experiences.
These digital assets blur the line between physical and virtual economies, expanding the market for creativity and entrepreneurial opportunity.
Discover Global Streaming Wars: The Battle for Cultural Influence to compare how virtual content builds new global markets.
The Challenges: Regulation, Ethics, and Inequality
Despite its promise, the metaverse faces significant challenges. Data privacy and security remain major concerns, particularly as companies collect vast amounts of biometric and behavioral information. The potential for digital harassment, surveillance, and manipulation raises serious ethical questions.
Regulation is another pressing issue. As virtual economies grow, governments must determine how taxation, intellectual property rights, and consumer protection apply to digital transactions. Without clear frameworks, the metaverse may become vulnerable to cybercrime, fraud, or illicit financial activity.
Digital inequality also threatens to deepen global divides. Access to high-speed internet, modern devices, and advanced hardware varies widely across countries. If the metaverse becomes central to work and education, regions without strong digital infrastructure could be left behind. Ensuring inclusive access will be critical for making the metaverse a truly global economic system.
Consider Why Cybersecurity Is Becoming a Global Priority to look at the risks in hyper-connected virtual systems.
A Glimpse of the Future Digital World
The metaverse remains in its early stages, but its trajectory is becoming increasingly apparent. It will not replace the physical world but augment it by layering digital experiences onto daily life in ways that enhance work, learning, healthcare, and social interaction. Companies that invest in metaverse-ready strategies may gain competitive advantages, while individuals will find new pathways for creativity and economic participation.
The global economy is entering a hybrid future where physical and virtual spaces coexist. Beyond gaming, the metaverse is becoming a cornerstone of innovation and a frontier that will shape the next era of digital globalization.